ERP Implementation: A Comprehensive Guide for Seamless Business Optimization
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of business, organizations are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. One transformative solution that has emerged is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) implementation. ERP systems integrate various business functions into a single, centralized platform, providing a comprehensive view of an organization’s operations. This article delves into the complexities of ERP implementation, exploring its advantages, challenges, and essential considerations for successful execution.
What is ERP Implementation?
ERP implementation is the process of integrating an ERP system into an organization’s existing infrastructure and business processes. It involves a comprehensive assessment of the organization’s needs, customization of the ERP software, data migration, user training, and ongoing maintenance. ERP implementation aims to automate and streamline business processes, eliminate data silos, and provide real-time insights into the organization’s performance.
Advantages of ERP Implementation
- Streamlined Operations: ERP systems centralize data and processes, eliminating the need for multiple disparate systems. This reduces manual errors, improves communication, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
- Improved Data Management: ERP systems provide a single source of truth for all business data, ensuring data integrity and consistency. This enables organizations to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information.
- Enhanced Collaboration: ERP systems facilitate seamless collaboration between different departments within an organization. Real-time data sharing and integrated workflows improve coordination and reduce the time required for decision-making.
- Increased Productivity: ERP systems automate repetitive tasks and reduce the need for manual data entry. This frees up employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities, boosting productivity and innovation.
- Improved Customer Service: ERP systems provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions across all channels. This enables organizations to respond promptly to customer inquiries, resolve issues effectively, and enhance the overall customer experience.
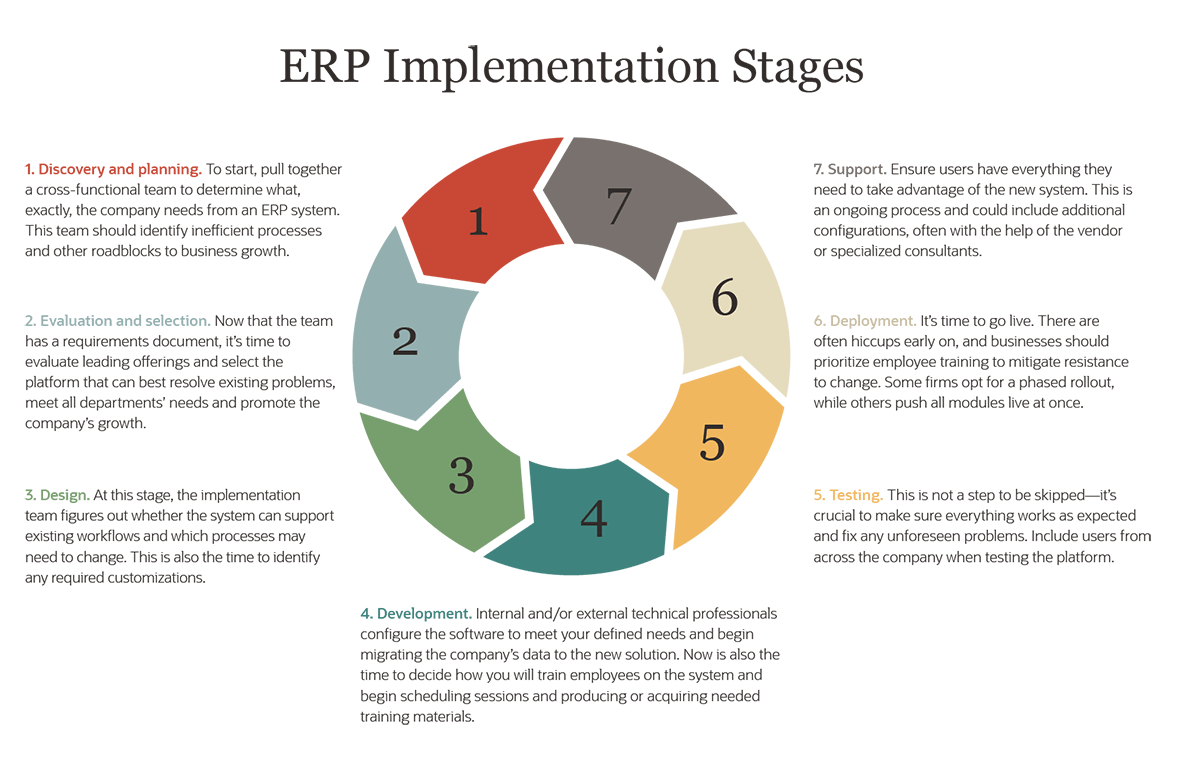 .
.
Disadvantages of ERP Implementation
- High Implementation Costs: ERP implementation can be a significant investment, involving software licensing fees, hardware upgrades, and consulting services. Organizations need to carefully assess the return on investment (ROI) before committing to an ERP project.
- Complexity and Time-Consuming: ERP implementations are complex and time-consuming processes that can disrupt daily operations. Organizations need to allocate adequate resources and plan for potential disruptions during the implementation phase.
- Data Migration Challenges: Migrating data from legacy systems to an ERP system can be challenging and time-consuming. Organizations need to ensure data accuracy and integrity throughout the migration process.
- User Resistance: Resistance to change is a common challenge during ERP implementations. Organizations need to involve users in the planning and implementation phases to address concerns and ensure successful adoption.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Updates: ERP systems require ongoing maintenance and updates to ensure optimal performance. Organizations need to factor in the costs and resources required for ongoing support and upgrades.
 .
.
Essential Considerations for Successful ERP Implementation
- Clear Business Objectives: Define the specific business objectives that the ERP implementation aims to achieve. This will guide the selection, customization, and implementation of the ERP system.
- Thorough Planning and Analysis: Conduct a thorough assessment of the organization’s existing business processes, data requirements, and infrastructure. This will help identify areas for improvement and ensure a smooth transition to the ERP system.
- Vendor Selection and Customization: Carefully evaluate different ERP vendors and select the one that best aligns with the organization’s needs. Customize the ERP software to fit the specific requirements of the organization.
- Data Migration and Integration: Develop a comprehensive data migration plan to ensure the accuracy and integrity of data during the transition to the ERP system. Integrate the ERP system with other business systems to create a seamless flow of information.
- User Training and Adoption: Train users thoroughly on the new ERP system and provide ongoing support to ensure successful adoption. Address user concerns and resistance to change to foster a positive and productive work environment.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Support: Establish a plan for ongoing maintenance, updates, and support of the ERP system. This will ensure optimal performance and minimize disruptions to business operations.
Conclusion
ERP implementation is a transformative journey that can bring significant benefits to organizations. By carefully considering the advantages, challenges, and essential considerations outlined in this article, organizations can navigate the implementation process effectively and maximize the value of their ERP system. Remember, ERP implementation is not just a technology investment; it is a strategic initiative that can revolutionize the way organizations operate and compete in today’s dynamic business environment.
 .
.

