ERP vs. CRM: A Comprehensive Guide to Enterprise Software
Introduction
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations must leverage technology to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. Two essential enterprise software solutions that play a crucial role in this transformation are Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM). Understanding the differences between ERP and CRM is paramount for businesses seeking to optimize their technology investments and achieve their strategic objectives.
ERP: A Comprehensive Business Management Solution
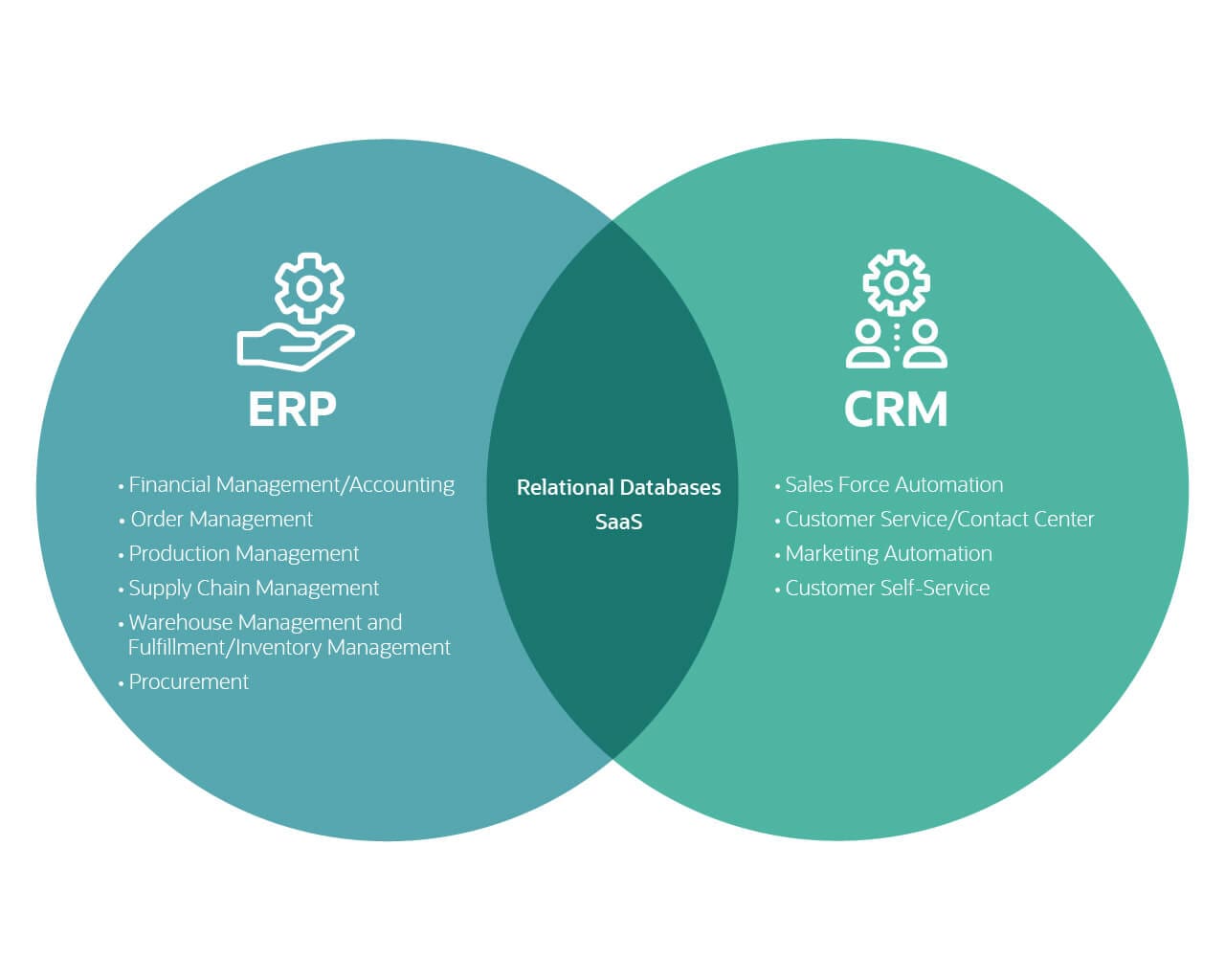
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is an integrated software suite that centralizes and streamlines all core business processes, including:
- Financial Management: Tracks financial transactions, manages accounts payable and receivable, and prepares financial statements.
- Human Capital Management: Automates HR processes such as employee onboarding, payroll, and performance management.
- Supply Chain Management: Optimizes inventory management, purchasing, and logistics.
- Manufacturing: Manages production planning, scheduling, and quality control.
- Sales and Marketing: Provides tools for lead generation, opportunity tracking, and order management.
 .
.
CRM: Focusing on Customer Interactions
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a software solution designed to manage and nurture relationships with customers. It provides a centralized platform for:
- Sales Management: Tracks sales opportunities, manages customer accounts, and automates sales processes.
- Marketing Automation: Creates and executes marketing campaigns, tracks customer interactions, and generates leads.
- Customer Service: Provides a central repository for customer data, enables case management, and offers self-service options.
- Analytics and Reporting: Generates reports and insights on customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness.
Advantages of ERP vs. CRM
 .
.
Advantages of ERP:
- Integrated Platform: ERP centralizes all business processes, eliminating data silos and improving data integrity.
- Real-Time Visibility: Provides real-time visibility into all aspects of the business, enabling informed decision-making.
- Improved Efficiency: Automates and streamlines processes, reducing manual tasks and increasing productivity.
- Reduced Costs: Eliminates redundant systems and processes, leading to cost savings in IT and operations.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration between different departments, breaking down barriers and improving communication.
Advantages of CRM:
- Customer-Centric Focus: CRM focuses on understanding and meeting customer needs, improving customer satisfaction.
- Improved Sales Performance: Provides tools to manage sales pipelines, track customer interactions, and close deals faster.
- Enhanced Marketing Effectiveness: Enables targeted marketing campaigns, personalized messaging, and lead nurturing.
- Improved Customer Service: Provides a centralized platform for managing customer interactions, resolving issues, and building relationships.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: Nurturing customer relationships leads to increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
Disadvantages of ERP vs. CRM
Disadvantages of ERP:
- High Implementation Costs: ERP systems can be complex and expensive to implement, requiring significant upfront investment.
- Complex to Use: ERP systems may require extensive training and ongoing support to ensure effective use.
- Lack of Customization: ERP systems are often designed for a wide range of industries, which may limit their ability to meet specific business needs.
- Data Overload: ERP systems can generate vast amounts of data, which can be overwhelming and difficult to manage.
- Long Implementation Timelines: ERP implementations can be lengthy and disruptive, requiring careful planning and execution.
Disadvantages of CRM:
- Limited Integration: CRM systems may not integrate seamlessly with other business systems, creating data silos and inefficiencies.
- Data Security Concerns: CRM systems store sensitive customer data, which requires robust security measures to prevent breaches.
- User Adoption Challenges: CRM systems require user buy-in and adoption to be effective, which can be challenging to achieve.
- Overreliance on Sales: CRM systems may focus primarily on sales processes, neglecting other aspects of customer management.
- Limited Scalability: CRM systems may not scale effectively as a business grows, requiring additional investment and customization.
ERP vs. CRM: A Summary
| Feature | ERP | CRM |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Business Processes | Customer Relationships |
| Key Functions | Financial Management, Supply Chain Management, Manufacturing | Sales Management, Marketing Automation, Customer Service |
| Benefits | Integrated Platform, Real-Time Visibility, Improved Efficiency | Customer-Centric Focus, Improved Sales Performance, Enhanced Marketing Effectiveness |
| Disadvantages | High Implementation Costs, Complex to Use, Limited Customization | Limited Integration, Data Security Concerns, User Adoption Challenges |
| Ideal for | Large Enterprises, Complex Business Processes | Small to Medium Businesses, Customer-Facing Organizations |
FAQs
1. What are the key differences between ERP and CRM?
ERP focuses on streamlining business processes, while CRM focuses on managing customer relationships.
2. Which system is right for my business?
ERP is suitable for large enterprises with complex business processes, while CRM is ideal for businesses that prioritize customer management.
3. Can ERP and CRM systems be integrated?
Yes, ERP and CRM systems can be integrated to provide a comprehensive solution for both business operations and customer management.
4. What are the benefits of integrating ERP and CRM systems?
Integration eliminates data silos, improves customer insights, and streamlines sales and marketing processes.
5. What are the challenges of implementing ERP and CRM systems?
Implementation can be complex and costly, requiring careful planning, training, and ongoing support.
6. How can I ensure successful implementation of ERP and CRM systems?
Involve stakeholders, define clear objectives, secure executive buy-in, and partner with experienced implementation consultants.
7. What are the latest trends in ERP and CRM software?
ERP and CRM systems are evolving towards cloud-based solutions, artificial intelligence, and mobile accessibility.
8. How can I measure the ROI of ERP and CRM investments?
Track metrics such as increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced operational costs.
9. What are the best practices for using ERP and CRM systems?
Establish clear processes, train users thoroughly, leverage automation features, and monitor system performance regularly.
Conclusion
ERP and CRM systems play a vital role in modern business operations, providing organizations with the tools to optimize processes, enhance customer relationships, and gain a competitive edge. By understanding the differences between ERP and CRM, businesses can make informed decisions about their technology investments and tailor their solutions to meet their specific needs.
Disclaimer
This article provides general information about ERP and CRM systems. The specific requirements and benefits of these systems may vary depending on the size, industry, and business objectives of an organization. It is recommended to consult with an experienced technology consultant or software vendor to determine the best solution for your business.
 .
.

