Navigating the Labyrinth of ERP Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide for Informed Decision-Making
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of business operations, the implementation of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solution has become paramount for organizations seeking to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. ERP systems act as the central nervous system of an enterprise, seamlessly integrating critical business functions and providing a unified platform for data management and analysis. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of ERP solutions, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, essential components, and implementation considerations to empower you with the knowledge necessary for informed decision-making.
What is an ERP Solution?
An ERP solution is a comprehensive software suite that integrates various business processes, including finance, supply chain management, manufacturing, human resources, and customer relationship management, into a single, unified system. It serves as a central repository for all critical business data, enabling real-time visibility and streamlined collaboration across departments.
Benefits of ERP Solutions
1. Enhanced Data Management and Analysis
ERP systems centralize all business data into a single, integrated database, providing a comprehensive view of the organization’s operations. This eliminates data silos and inconsistencies, ensuring data accuracy and integrity. Robust reporting and analytics capabilities empower businesses to gain valuable insights, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
2. Improved Process Efficiency
By automating and streamlining business processes, ERP systems eliminate manual tasks, reduce errors, and enhance productivity. Automated workflows and centralized data access enable seamless collaboration between departments, reducing communication delays and bottlenecks.
 .
.
3. Increased Visibility and Control
ERP systems provide real-time visibility into all aspects of the business, from financial performance to inventory levels. This comprehensive oversight empowers decision-makers with the necessary information to make timely and informed decisions, respond swiftly to market changes, and mitigate risks.
4. Enhanced Customer Relationship Management
Integrated CRM modules within ERP systems enable businesses to manage customer interactions, track sales opportunities, and provide personalized experiences. This centralized approach improves customer satisfaction, increases sales conversion rates, and fosters long-term relationships.
5. Reduced Costs and Improved Scalability
ERP systems can significantly reduce operational costs by eliminating manual processes, reducing inventory waste, and optimizing supply chain management. Additionally, ERP solutions are designed to be scalable, accommodating business growth and evolving needs without the need for costly customizations or system overhauls.
Disadvantages of ERP Solutions
1. High Implementation and Maintenance Costs
ERP implementations can be complex and expensive, requiring significant investment in hardware, software, and consulting services. Ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs should also be factored into the total cost of ownership.
2. Complexity and Customization Challenges
ERP systems are complex and require extensive customization to align with specific business requirements. This process can be time-consuming and costly, and it may involve trade-offs between functionality and ease of use.
 .
.
3. Data Migration and Integration
Migrating existing data from legacy systems into the ERP system can be a challenging and error-prone process. Data integration with third-party applications may also require additional development and maintenance efforts.
4. Resistance to Change and Training Requirements
ERP implementations can disrupt existing business processes and require significant training for users to adapt to the new system. Resistance to change and a lack of user adoption can hinder the successful realization of ERP benefits.
5. Vendor Lock-in and Dependency
Once an ERP system is implemented, businesses may become dependent on the vendor for ongoing support, upgrades, and customizations. This dependency can limit flexibility and increase the cost of future changes or upgrades.
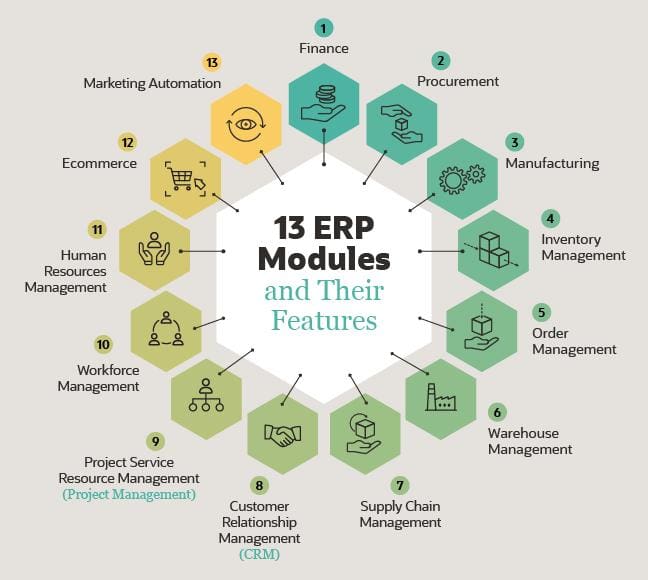
Essential Components of ERP Solutions
1. Financial Management
ERP systems provide comprehensive financial management capabilities, including general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, cash management, and financial reporting.
2. Supply Chain Management
ERP systems manage the entire supply chain, from procurement and inventory management to order fulfillment and logistics.
3. Manufacturing
ERP systems support manufacturing operations, including production planning, scheduling, quality control, and inventory management.
4. Human Resources
ERP systems manage HR functions such as payroll, benefits administration, employee self-service, and talent management.
5. Customer Relationship Management
ERP systems provide CRM functionality, including sales management, marketing automation, and customer service.
6. Business Intelligence and Analytics
ERP systems offer robust reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling businesses to gain insights into their operations and make informed decisions.
7. Integration and Extensibility
ERP systems can integrate with third-party applications and extend their functionality through add-ons and customizations.
Implementation Considerations
1. Business Process Analysis
Thoroughly analyze existing business processes to identify areas for improvement and align the ERP system with specific requirements.
2. Vendor Selection
Evaluate ERP vendors based on their industry expertise, product capabilities, implementation experience, and support services.
3. Data Migration and Integration
Plan a comprehensive data migration strategy to ensure accurate and timely transfer of data from legacy systems.
4. User Training and Adoption
Provide comprehensive training to users and encourage their active participation in the implementation process to foster user adoption and maximize system utilization.
5. Change Management
Develop a change management plan to address resistance and facilitate a smooth transition to the new ERP system.
Conclusion
ERP solutions offer a transformative opportunity for businesses seeking to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. By carefully considering the advantages, disadvantages, essential components, and implementation considerations outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can make informed decisions that will empower your organization to reap the full benefits of ERP technology.
Remember, the journey to ERP success is an ongoing one, requiring continuous optimization and adaptation to evolving business needs. By embracing a proactive approach to ERP management, you can ensure that your system remains a strategic asset, driving innovation, growth, and profitability for your organization.
 .
.

